
To fix this error, you need to reformat the USB disk with a macOS disk format such as Mac OS Extend(Journaled). Can’t copy because file is too large Mac? To overcome the 4GB size limitation, you must reformat the external drive using the HFS+ file format. How do I move files larger than 4GB FAT32 on Mac?įAT32 has a file size limit of 4GB, and if you attempt to transfer a file larger than that, an error occurs.

How do you fix the item cant be copied because it is too large for the volume’s format?.

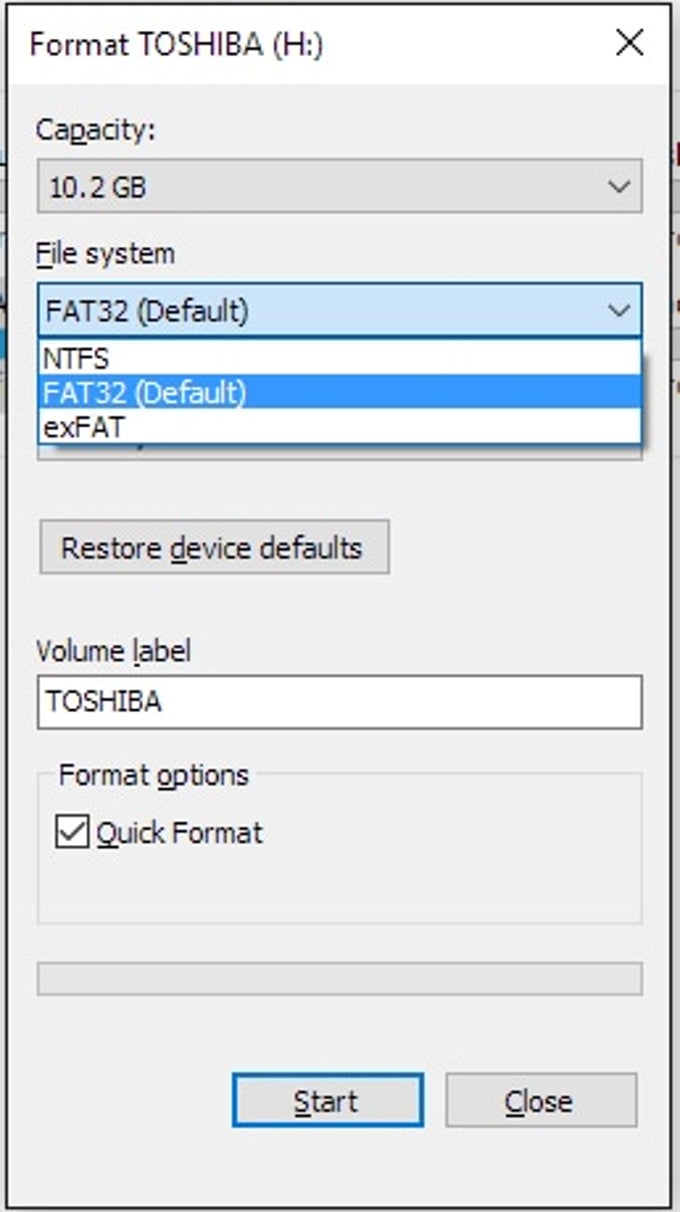
How do you fix the item can’t be copied because it is too large for the volume’s format?.How do I transfer files larger than 4GB to USB Mac?.Can’t copy because file is too large Mac?.How do I move files larger than 4GB FAT32 on Mac?.You can also check the name of the storage device by running the df -h command. The system will mount your newly formatted drive with the name you specified in the command. Once the formatting is complete, physically unplug the storage device from your computer and then plug it in again. The FAT32 file system is compatible with all mainstream operating systems.Īpart from the FAT32 file system, other file system formats you can use for formatting your storage device include ext, Minix, MS-DOS, etc. In this case, it will be MUO and the physical address mount point /dev/sda1. Also, you can specify the new name or label of the USB flash drive. The aforementioned command formats the specified drive using the FAT32 file format. The mkfs command builds a file system on a storage device according to the options specified. To format your storage device, use the mkfs (Make filesystem) command. Make sure to get the correct mount point of your device on your system. Note: In this case, /dev/sda1 is the physical address on which the storage device that we want to format is mounted. To unmount the storage device, you can use the umount command as below. For optimal efficiency when formatting, it is important you unmount your storage device first. When your storage device is mounted on your system, Linux assumes the drive to be of a fixed size and specific format. Most Debian-based distros like Ubuntu will list the drive on the files menu. Your USB flash drive will be listed under the files menu or on the desktop depending on your desktop environment. If for some reason, the device is not automatically mounted, here is how you can mount the drive in Linux. Most Linux desktops will automatically mount your storage device once you connect it to your computer. Just make sure that you backup your data before formatting the device. Note that the steps are the same for other storage devices as well. If you wish to follow along, the best way is to practice using a USB flash drive. Note: Always exercise caution when formatting drives to avoid losing important information. Some reasons you might want to do this include: to get rid of malicious software, improving performance, or removing sensitive data before handing over the storage device to another person. When you format a storage device, you are essentially deleting all data or information stored on that device, more like restoring it back to its default factory settings.
#HOW TO FORMAT USB DRIVE FAT32 MAC HOW TO#
This guide will show you how to format a storage device right from the Linux terminal. Some of the most common ones include external or internal hard drives, flash disks, CDs, etc. Used for storing processed data, storage devices come in many different forms. A storage device is an integral part of your computer hardware and computing in general.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
